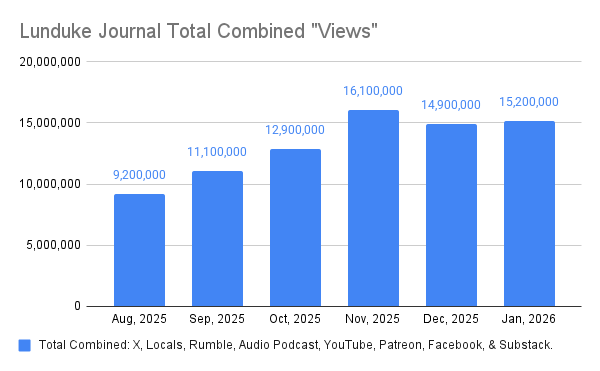
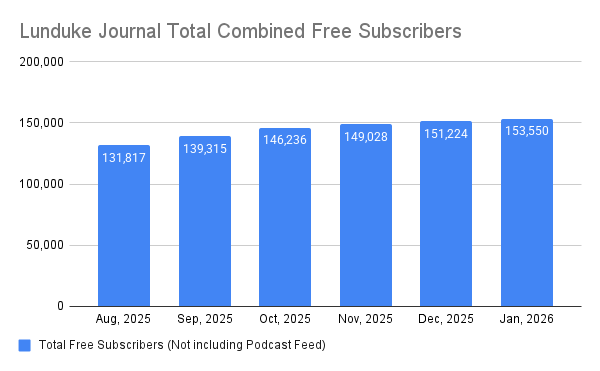
The HP 100 / 200 LX palmtops are nothing short of spectacular little machines. Pocket-sized, clamshell, battery powered, MS-DOS computers — with a fascinating (and highly useful) array of hardware and software.
Want to use a modem? Expand storage and functionality with a PCMCIA card? Run full DOS software — and even Windows 3.0 — on the go? All were possible with these little, hand-held marvels.
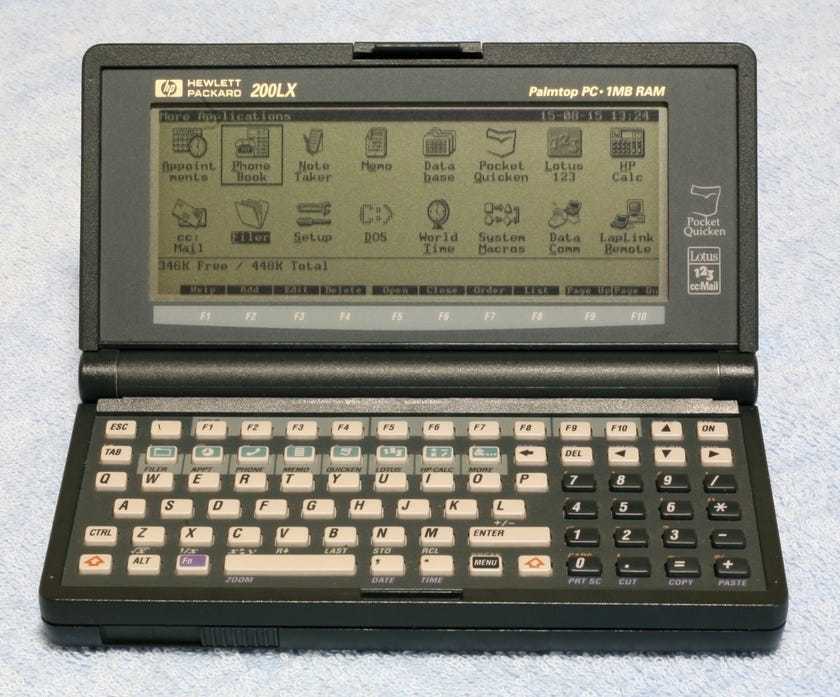

And, when I say, “Run Windows 3.0”… I really mean it. Here is a picture taken by a Lunduke Journal Community member of their own, personal HP 200LX. Running a full edition of Windows 3.0 (in Real Mode — the 200LX’s 80186 CPU doesn’t support Protected Mode).

But how did these amazing little pocket computers come to be? Let’s take a little tour of the history of the HP LX line, which all started in 1988 at Hewlett-Packard… with a product idea code-named “Cheetah”.
Note: Much of this history is compiled from the notes and memories of Everett Kaser, a programmer who worked on this project (and many others) at HP, combined with bits and pieces gleaned over years of study of these wonderful computers.
1988 - Codename “Cheetah”
It all started in Corvallis, Oregon — a small city, around an hour and a half outside of Portland, Oregon — at the office known as the “Corvallis Division”.

The Corvallis Division had already seen some noteworthy success in developing multiple HP computers, including the HP 85A in 1980:

The original idea for “Cheetah” was to be a personal information manager pocket device, powered by the Saturn CPU — which was already in use by multiple HP calculators and ranged from 640 kHz up to around 8 MHz.
What’s more, the entire system would run on just 32KB of RAM and use a nearly identical physical design to the HP 19B calculator (with a vertical clamshell design, with a keyboard on the left).

1989 - Codename “Jaguar”
In early 1989, the team made the decision to come up with a new physical form factor. It was at this point that the codename for the project was changed to “Jaguar”.
Instead of keeping to the same look of the HP 19B seen above… they would make a design using a more standard clamshell — with a screen on top, and keyboard on bottom. Like a traditional laptop. But pocket-sized.
And thank heavens they made that change. Because it just wouldn’t have been as cool had they stuck with that original, side-by-side design.
Everything else, though, still remained the same. The Saturn CPU. Not running DOS. Basically just a calculator… but with a lot of personal information management type software built in.
It was also decided that this device needed a spreadsheet program. An idea that would radically alter the direction of the project.
Lotus 1-2-3 leads to MS-DOS
Imagine yourself back in 1989. Now. When I say “Spreadsheet Software”… who do you think of?
You think of Lotus 1-2-3. That’s who.
And, as luck would have it, Lotus had an internal goal of working with a hardware vendor to create what they called a “Portable 1-2-3 Machine”. It seemed like a match made in heaven! HP could develop the hardware and some of the software, and Lotus could provide 1-2-3 (and also develop some of the other software components).
There was just one problem: Lotus 1-2-3 didn’t run on the (very limited) Saturn CPU. It ran on DOS. With an Intel 8086 class CPU.
So the team at HP made the — incredibly wise — decision to ditch the Saturn CPU and turn the “Jaguar” project into a DOS compatible computer. Intel processor and all.
Initially, while “Jaguar” was going to be DOS compatible… they were not going to allow any random DOS software to run. It was going to be locked down to only run the software supplied on the ROM of the device (from HP and Lotus). Quickly this was relaxed, and the ability to drop to a standard MS-DOS prompt was added.
Because… it was iust such an obvious thing to do.
1991 - The HP 95LX
Development of this new 8086, DOS powered device — now dubbed “Jaguar II” — moved ahead at an incredibly fast pace, with the release planned to happen just 13 months after the basic specs were decided upon. Software, hardware, all of it.
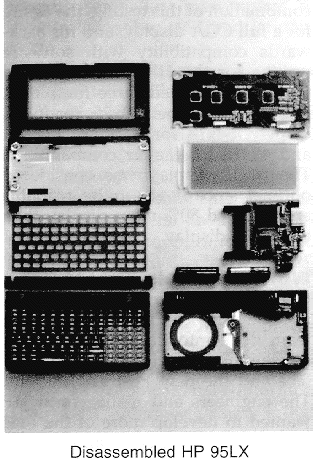
In the end, the HP 95LX managed to ship just a couple months later than planned — in April of 1991. Which is darned impressive considering the massive investment in both hardware and software.
The final 95LX shipped with an NEC V20 CPU (which was an 8088 compatible processor at 5.37 MHz), 1MB of RAM, and up to 32MB of removable storage. The operating system was MS-DOS 3.22, which booted from ROM.
All of this was powered by AA batteries. Which, let’s face it, is pretty cool.
It included a host of custom built, personal information management software and — of course — Lotus 1-2-3.
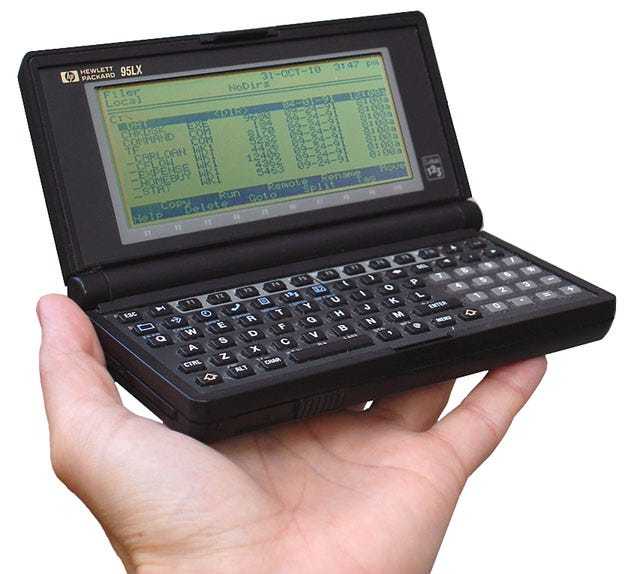

Just look at it. Full QWERTY keyboard. Even has a 10-key numeric keypad. And Function keys. It might be a small keyboard, with little membrane keys… but it’s complete and surprisingly usable. It even has arrow keys (see the top right of the keyboard).
But it wasn’t perfect. Not yet.
The HP 95LX was an impressive (and incredibly fun to use) little DOS palmtop. But it had some problems.
The first was the display. A non-standard 240x128 LCD (with a 40x16 text mode). This presented significant compatibility issues with existing DOS software.
The second was the speed. The 8088 compatible CPU was a bit… to put it mildly… pokey. And a great deal of existing software simply required more oomph.
The third was battery life. It wasn’t bad, running off a set of AA batteries. But the team knew they could do better.
1993 - HP 100LX - Codename "Cougar"
Over the next two years the team worked to fix those problems — all while refining and improving the built-in software.
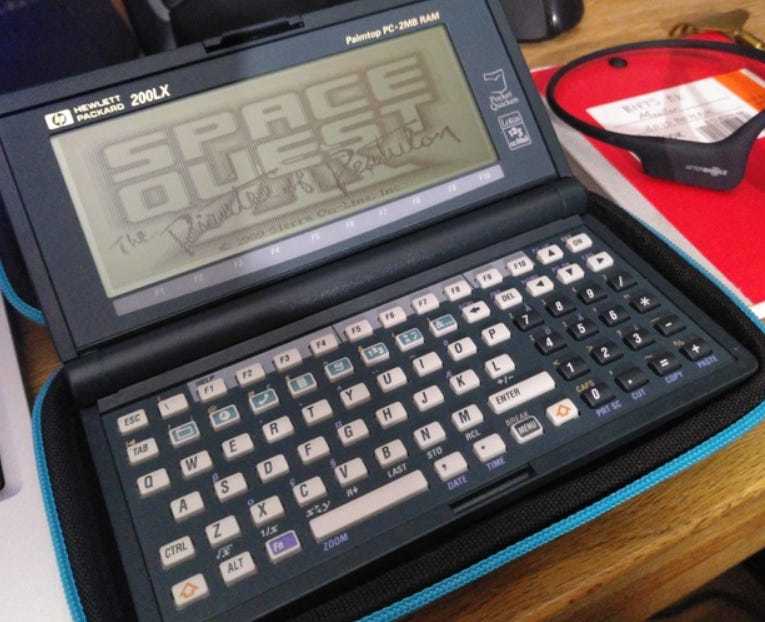
The, rather funky, 240x128 display of the 95LX was ditched for a standard, monochrome CGA display at 640×200. This allowed for greatly enhanced software compatibility with existing DOS software. Including, believe it or not, games.
For example here is Space Quest 3 running on an HP 200LX (which is using the same display and CPU of the HP 100LX):

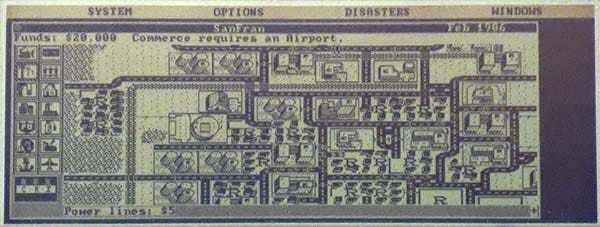
And here is a snapshot of SimCity running on the built-in CGA display:
The NEC V20 “8088” CPU was swapped out for an 80186 compatible CPU (a “Hornet”) running at a higher clock speed. This was a significant boost in both horsepower and CPU functionality — which allowed the running of many software applications that traditionally required an 80286 processor.
Then the voltage was dropped from 5V to 3V. Effectively giving a significant gain in battery life.
Of course there was also the software upgrades — both to the included, in-house developed launcher and an upgrade to MS-DOS version 5.0.
All of which combined to make the 100LX and 200LX (which were nearly identical in most ways) extraordinarily compatible with desktop DOS-compatible PCs. Considering all of this was powered by two AA’s and could fit in your pocket?
Nothing short of spectacular.
And, to think, this all started out as what was — essentially — a nice HP calculator with some personal information manager stuff built-in.
Thank heavens the team decided they needed a spreadsheet.