Over the last two decades, Wikipedia has become one of the most visited -- and most referenced --websites on Earth.
And nearly every one of us is familiar with Wikipedia's regular requests for donations, often including urgent-sounding text along the lines of "protect Wikipedia's independence" and "without reader contributions, we couldn’t run Wikipedia."
Sounds pretty dire, right? Wikipedia must be in pretty rough shape! They need those donations right away! If I don't donate, they might need to shut down! Surely they run a pretty tight ship, with some pretty lean and mean operations... right? And surely -- surely -- the funds they have are being handled in a transparent way!
You know what?
Just for kicks, let's take a look at the finances of Wikipedia -- using all publicly available sources of documentation (including IRS filings, annual reports, and audits) -- and see what the real financial state of Wikipedia is like.
Because this is The Lunduke Journal. And that's what we do.
Spoiler: It's all really, really weird. And highly sketchy. Also a ton of money donated for Wikipedia... isn't used to run Wikipedia.
The Wikimedia Foundation
The financial core of Wikipedia is the Wikimedia Foundation. The Foundation, itself, is responsible for running the actual Wikipedia servers -- and that is where everything else branches out from.
Let's start with the most basic piece of information we need:
How much money does The Wikimedia Foundation receive, in donations, every year -- from people who believe they are directly funding the Wikipedia servers?
According to the most recent IRS filings (2021)... roughly $164 Million USD for the year.
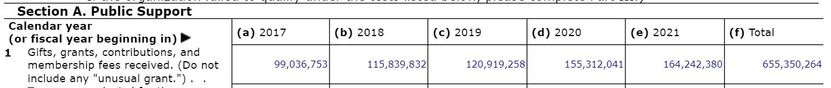
Year-on-year, Wikimedia is seeing significant growth -- with each year recording record donations. Up an additional $9 Million between 2020 and 2021 alone.
While those numbers seem large, at first glance, they really only tell a small part of the story.
What if -- for example -- Wikipedia needs even more than $164 Million, every single year, to operate? What are the various expenses of Wikipedia?
Luckily, we have a high level breakout of expenses in the yearly Wikimedia Foundation audit.
Turns out, the costs associated with the server hosting of Wikipedia for 2021 was just shy of $2.4 Million.
But server hosting costs are only part of the equation, right? There's also other wages, travel, and all manner of expenses. So let's add it all up.
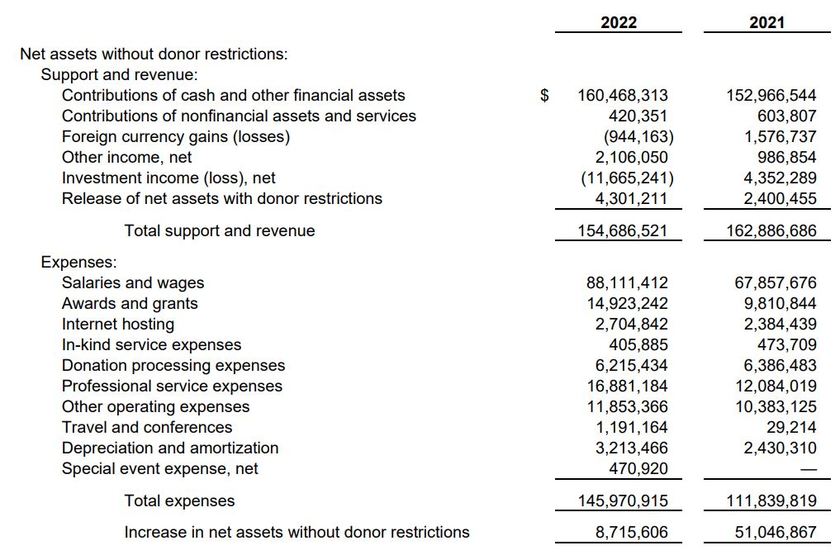
After all is said and done -- and all revenue and expenses are taken into consideration -- The Wikimedia Foundation received over $50 Million dollars more than they spent in 2021.
They made $50+ million in profit.
Doesn't sound like an organization that is hurting for funding... does it?
Let's take a look back over the last few years (starting in 2015) and chart out the yearly financials of Wikimedia. It shows some absolutely astonishing growth in terms of total assets (such as money in the bank).
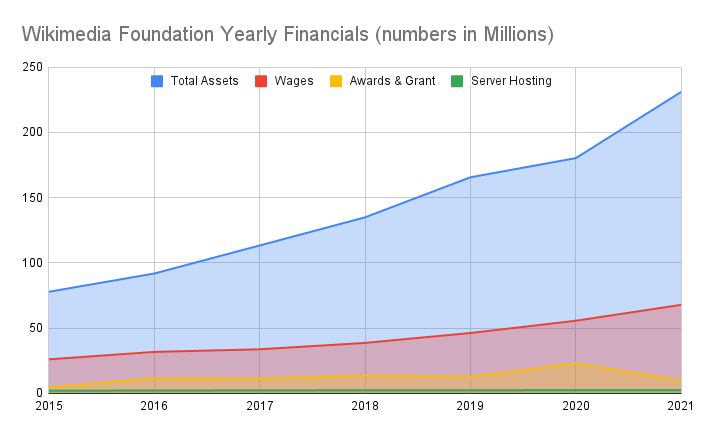
A few items worth noting:
- Server Hosting related costs for all Wikipedia related sites was $2 Million in 2015. It has remained mostly flat (compared to income and other costs) only raising to $2.4 Million as of 2021.
- As of 2021, Wikimedia has over $231 Million in assets. And growing... rapidly. Just look at that blue line!
- Assets and profit are growing, despite a massive increase in Salaries and Wages: from $26 Million in 2015... to $67.8 Million in 2021.
So. Let's answer a burning question:
Q: Does Wikipedia desperately need your donations in order to continue operating?
A: No. Not by a long-shot. If donations dropped significantly, there would be no hit to Wikipedia operations. Certainly not for quite some time.
When Wikipedia tells you they need your $5 donation to keep running? They are lying to you.
In fact... this is just the tip of the iceberg.
There are also two unique financial entities, related to Wikimedia, that are... extremely strange: The Wikimedia Endowment and The Knowledge Equity Fund.
Let's take a look at those.
The Wikimedia Endowment
Back in 2016, The Wikimedia Foundation establed "The Wikimedia Endowment" -- with a goal of stockpiling $100 Million dollars worth of funding within the endowment.
So what is the stated goal of The Wikimedia Endowment?
"The Wikimedia Endowment is our enduring commitment to a world of freely shared knowledge, now and in perpetuity."
Ok. Vague. But that tends to be the way with these sorts of foundations.
What sort of work actually gets funded by this Endowment? According to their website... they only give a list of "select projects". Not a complete list. And we also don't have any details of how much this Endowment spends on any given project.

Not specific. Not transparent. No amounts given. Or dates. Or... much of anything.
But we do know that the Endowment has met its $100 Million funding goal (and still growing) as of 2021:
"as of December 31, 2021, the Endowment held $105.4 million ($99.33 million in an investment account and $6.07 million in cash), with an additional $8 million raised in December 2021 due to be transferred to the Endowment in January 2022."
Now... here's where The Wikimedia Endowment starts to get... weird.
From the time the Endowment was created, in 2016, to 2021... The Wikimedia Foundation deposited $5 Million dollars (of Wikipedia donations) into the Endowment. Totalling $30 Million according to the most recent Wikimedia Foundation Audit.

But... wait. Wait. Wait.
Two big questions crop up from that paragraph from the 2021 audit:
- If Wikimedia Foundation only contributed $30 Million (from user donations) to the Endowment... who contributed the rest of the money? A company? Rich benefactor?
- And what is this "Tides Foundation"?
Turns out, the benefactors of this Endowment are absolutely fascinating.
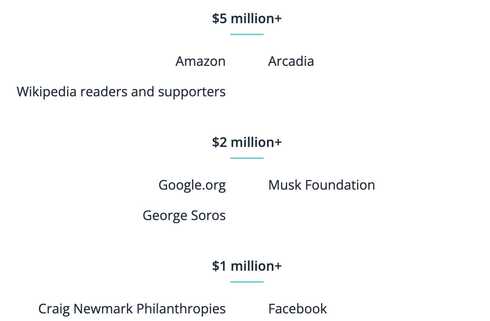
You read that right. George Soros. Yes, that George Soros. (Also Facebook & Google).
As for "The Tides Foundation", they run and manage the entire Wikimedia Endowment. All $100+ Million of it.
Here is a very intereting bit, from Wikimedia:
"The funds may be transferred from Tides either to the Wikimedia Foundation or to other charitable organisations selected by the Wikimedia Foundation to further the Wikimedia mission."
Go ahead. Read that sentence again.
That Wikimedia Endowment money? That 100 Million bucks? Could go to "other charitable organisations". What are those? Who knows! There's close to zero transparency about it.
Whoever the heck "Tides" is... they have an awful lot of power here when it comes to this "Wikimedia Endowment" money. Let's go further.
What, exactly, is Tides?
This is what Wikipedia says about Tides (it seemed an approriate place to reference):
"Tides Foundation is an American public charity and fiscal sponsor working to advance progressive causes and policy initiatives"
Yep. The Tides Foundation is a specifically political organization... for funding, organizating, and pushing specific political agendas.
Editorial Note: Here at The Lunduke Journal of Technology, we try our best to stay away from politics. As such, we will not be discussing some of the many, and varied, political stances of The Tides Foundation in any detail here. But, since Tides (and, as we will see, Wikimedia) are making pointed political statements and investments... The Lunduke Journal will be including those and letting you, the reader, make up your own mind about any political ramifications.
Is it strange that Wikipedia donations are being sent, by the Millions, to be handled by a political orgainzation? Yes. That is, most definitely, strange. Considering Wikipedia has repeatedly stated the importantce of neutrality... incredibly so.
But it gets... even weirder.
Neither Wikimedia nor The Tides Foundation publish details about how those funds are being used. It appears to be a secret. But, considering what The Tides Foundation does, it is something political. And only on one side of the political spectrum. Not neutral, like Wikipedia says they must be.
And the ties between Tides and Wikimedia go way, way beyond just managing a hundred million dollars...
In 2019, The Wikimedia Foundation hired a new General Council. Where did that person work in her previous job? You guessed it. The Tides Foundation. Seriously.
What do we know?
- The Tides Foundation manages and runs all $100+ Million of the Wikimedia Endowment.
- Donations to Wikipedia paid for roughly $30 Million of that Endowment (with the remainder coming from unknown sources).
- The Tides Foundation exclusively does political work for one part of the political spectrum.
- The connections between Wikimedia and Tides run deep.
- Neither Tides, nor Wikimedia, have published how that money is being used.
Which brings us to yet another area where Wikimedia is investing Wikipedia donations... in ways that are extremely political.
Once again: The Lunduke Journal of Technology is not going to tell anyone what they should think about any particular political views. The official stance of The Lunduke Journal is that extreme politics -- of any kind -- tend to not be a positive force in the running of software and other computing projects.
Knowledge Equity Fund
Let's talk about one more way that Wikipedia donations are spent. This concerns a much smaller amount of funds than we previously talked about with the Endowment... but the stated goals around it warrant documenting.
The "Wikimedia Foundation Knowledge Equity Fund" is a US $4.5 million fund created by the Wikimedia Foundation in 2020, to provide grants to external organizations that support knowledge equity by addressing the racial inequities preventing access and participation in free knowledge.
Here are some quotes, from the same Wikimedia page, to provide clarity around their goals:
"The Wikimedia Foundation defines racial equity as shifting away from US and Eurocentricity, White-male-imperialist-patriarchal supremacy, superiority, power and privilege"
"Racial equity aims to promote ... non-White, non-US ... communities"
Whatever your thoughts around any of those statements, it should be noted that Wikimedia is spending $4.5 Million dollars worth of Wikipedia donations to further those goals. Money that is not being spent on running Wikipedia.
In fact... it is worth noting that the dollar figure being allocated towards this "Knowledge Equity Fund" is twice the size of the yearly Server Hosting costs for all of Wikipedia.
What does all this mean?
Regardless of what any of us think about the specific political spending of Wikimedia, one thing is crystal clear:
A significant portion of donations -- solicited for the stated purpose of the running of Wikipedia -- are being spent furthing political goals. Not on running Wikipedia. All while Wikipedia is claiming to be barely surviving.
And Wikimedia is getting rich in the process.
Like this type of 100% independent Tech reporting? Be sure to subscribe to Lunduke.Locals.com. Even a free account is a good idea.
Here are a few other articles you might also find interesting: