On December 8th, 2022, the Linux Foundation released their annual report for 2022.
I’m not going to sugar coat this… it is absolutely ridiculous.
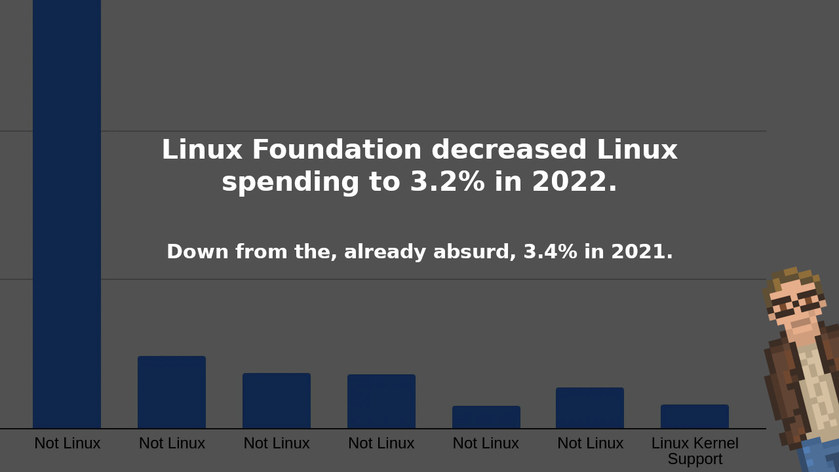
The highlight? Funding for the Linux kernel, in 2022, dropped to a measly 3.2% of the foundation’s total revenue of $243 Million dollars.
Down from the — already absurdly low — 3.4% from 2021.
Considering the name of the foundation… that is, needless to say, highly amusing. Or concerning. Possibly infuriating. Likely all three.
Let’s dive into the details and try to figure out why this is happening.
Seriously. Expenditures on Linux drop to 3.2%
Let’s dive into this deeper and try to get an understanding of exactly what is happening here… because that number is just so, dramatically low.
While The Linux Foundation keeps fairly tight-lipped about the details — and they haven’t published their IRS 990 forms for the last two years (which would provide us additional details) — they do provide some high level percentages for us to work from.
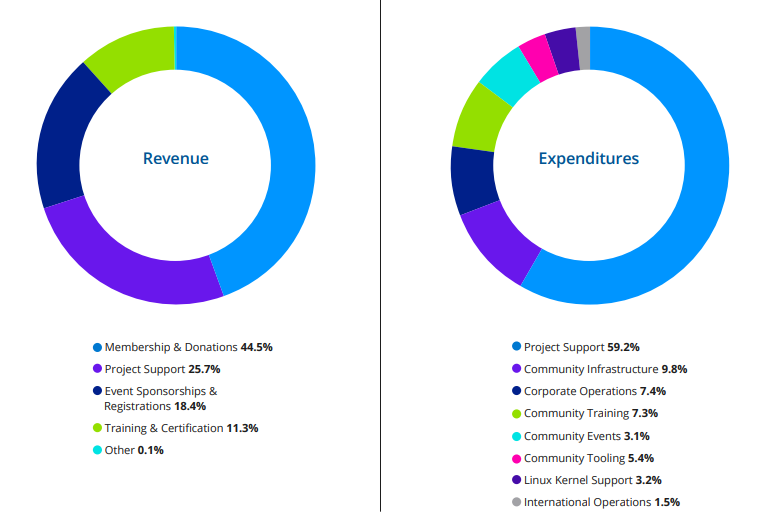
That chart on the right. The expenditures. Let’s zero in on those numbers and break it down into a bar chart to better visualize things.
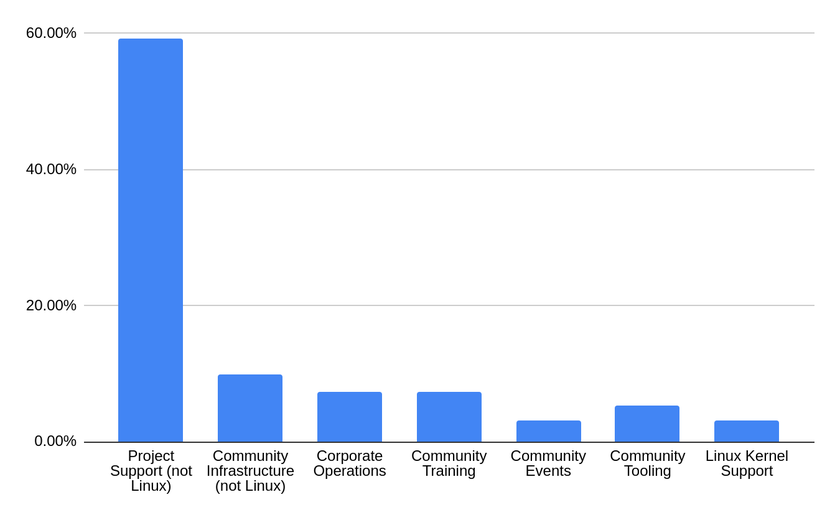
A few things you’ll immediately notice:
Linux is almost the smallest category that the “Linux Foundation” spends money on.
“Corporate Operations” receives over twice the funding that “Linux” does.
And non-Linux projects? Those receive nearly twenty times the funding of Linux. Twenty! 20x!
The Linux Foundation brought in over $243 Million USD in 2022. Which means the total amount put towards Linux was, according to The Linux Foundation, roughly $7.7 Million (3.2%).
For comparison, the Foundation spent roughly $18 Million on “Corporate Operations” and $144 Million on non-Linux projects.
It’s almost hard to wrap your head around, isn’t it? Here’s another chart that shows Linux Foundation spending.
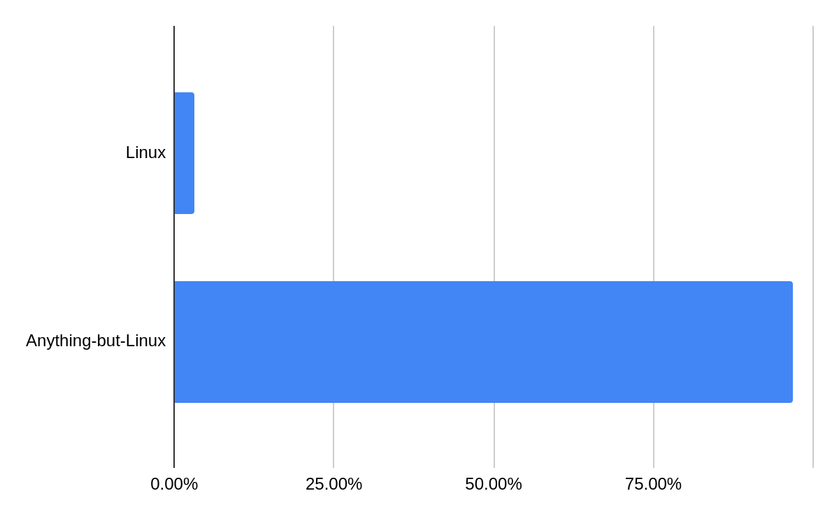
This is, needless to say, wild. And it calls up a few questions, namely:
What, exactly, is all that money being spent on?
And… why?
Who is making the decision to spend so much money on things that are not Linux?
Let’s see what we can find out.
Where is that money going?
Again, the Linux Foundation provides very few specific details. And hasn’t provided a publicly available form 990 -- an IRS filing required for all tax exempt organizations -- for the last two years (once they do, the Lunduke Journal of Technology will investigate the contents).
Instead, the Linux Foundation provides a generalized breakdown of project types and percentages in their annual report (which, despite being over 130 pages long… is light on actual numbers).
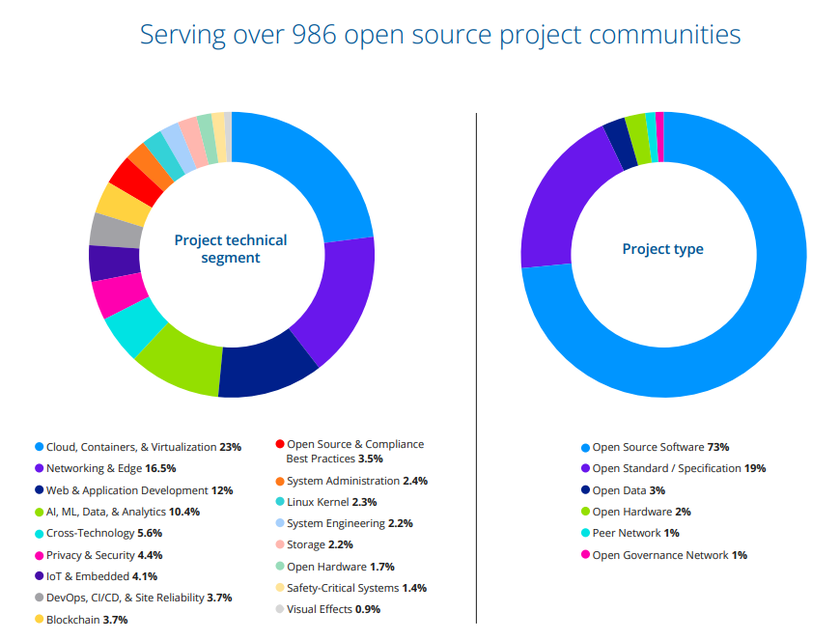
Highlights:
The Linux Foundation invests more money into “Blockchain” than “Linux”. By a lot (3.7% vs 2.3% of total project spending).
They also invest more — a lot more — in “Compliance Best Practices”, “AI”, “IoT”, and “Cloud”.
Repeat: “Blockchain” related projects receive nearly twice the funding of “Linux”… in the Linux Foundation.
I mean… What?!
Now, in defense of The Linux Foundation, the majority of that project funding is going towards open source software of one type or another. At least tangentially. Just not… you know… Linux.
Getting out of the Linux business
What are a few of the specific projects receiving that funding? Here’s four that have an entirely unknown amount of funding:
“LF Public Health” - tasked with creating vaccine passport systems.
“LF Energy” - tasked with climate change related initiatives.
“The Overture Maps Foundation” - tasked with creating a Google Maps alternative.
“The Open Metaverse Foundation” - tasked with creating a Facebook/Meta “Metaverse” competitor.
This is worth repeating: We do not have detailed financial information on these sub-foundations. They don’t provide individual annual reports for each (as they are all under the “Linux Foundation” umbrella) and there doesn’t appear to be any source of documentation, publicly available, to figure out those details.
The fact is, some of these projects may receive many times what the Linux kernel receives. Others may receive a tiny fraction of that amount. We simply don’t have that information.
And, without the Linux Foundation having publicly available 990 forms for 2022 (which are required for organizations like the Linux Foundation)… those vague, percentage breakdowns, by category, are the best bits of information we have available.
Which, honestly, is troubling.
But, one thing is clear, the Linux Foundation is investing — heavily — in almost any type of software… as long as it is not their core business... Linux.
If we were looking at any other company — that observation, combined with the decreasing percentage of revenue spent on their core product — would lead us to the obvious conclusion that they were getting out of their core business.
Which means… it looks like the Linux Foundation is preparing to get out of the “Linux” business.
I know. I know. Don’t shoot me.
I’m just pointing at what’s happening and saying out loud what we’re all thinking.
Where does that money come from?
Great. But… why is this happening? Why is so little funding actually making it to Linux? Why are they migrating — almost entirely — towards other businesses?
In an attempt to answer that, let’s look at where the money comes from — let’s figure out who actually controls the purse-strings.
According to the annual report, the largest block of income (44.5%) comes from membership in the Linux Foundation itself. And we know that becoming a “Platinum Member” of The Linux Foundation costs $500,000 per year.
So who, exactly, are those Platinum Members, you ask? We’ve got a handy graphic just for that!

Microsoft. Oracle. Meta (Facebook). Intel. Huawei. Tencent.
Drop down to the Gold level (which runs $100,000 per year) and you’ve got firms like Google, BlackRock, Cardano, Alibaba, WeBank, Refinitiv, Baidu, and many others.
Those memberships add up. Quickly. These are the companies that pay for the salary of those at The Linux Foundation.
Not only do those companies all have the ear of Linux Foundation executives (if someone gives you half a million dollars every year… you certainly pick up the phone when they call)… but those Platinum Members also get a seat on the Linux Foundation Board of Directors.
They pay... so they get to drive.
This is the current Board:

Take note of the companies that each Board Member represents and works for. (Also worth noting that the Board Chair, Nithya Ruff, works for Amazon… though that is not disclosed in that graphic.)
A lot of companies. And, at least some of those companies… would rather not see Linux succeed.
Note: I, Lunduke, know many of these people. I’ve broken bread with a rather large portion of them. Some of them I rather quite like personally. But all of them — every single one — has an agenda. Someone gives them a paycheck. And that’s worth noting.
And these are the people who — to a significant degree — determine which projects and sub foundations the Linux Foundation will create, promote, and fund. And which it won’t.
While we do not have publicly published meeting minutes — Oh! What we wouldn’t give to have been a fly on the wall of some of those meetings! — looking at the individuals (and companies they represent) on the board… we can clearly see why “Linux” funding is not only a small portion of what The Linux Foundation does… but it’s shrinking, year-on-year.
Without published minutes of the Linux Foundation board, and publicly available 990 forms for 2022, we are left in a position where the best we can do is piece together what little information is public… and draw our own conclusions.
And that conclusion is this: Many Mega Corporations have purchased influence in the Linux Foundation. And, as a result, the Linux Foundation is now transitioning away from Linux.
Pessimistic and cynical? For sure. But also rather obvious. In an undeniable way.
What is the future of Linux within The Linux Foundation?
Knowing what we know about The Linux Foundation — which is a whole lot less than we should know — what does the future of Linux support look like from the foundation?
Will we continue to see “Linux” becoming a smaller and smaller part of the overall Linux Foundation business?
The answer to that question seems to be a resounding: “Signs point to yes”.
In fact, I would not be surprised if they changed their foundation name to something without “Linux” in it… very soon.
If the Linux Foundation continues their current approach of establishing new sub-foundations (all focused on non-Linux activities and businesses)… My prediction is that 2023 will see growth in Linux Foundation total revenue, and another drop in Linux Kernel support — either in terms of total dollars or overall percentage. Possibly below 3%.
Note: The Lunduke Journal of Technology has reached out to the Linux Foundation with questions on these, and other, topics — and a request for comment. No response has been provided. Which is pretty par-for-the-course with stories concerning the Linux Foundation over the last several years.