Over the last year, there has been a tremendous amount of movement in terms of reported Linux marketshare -- with multiple reports showing Linux breaking 4% of the total desktop PC market during the last several months.
But what does that mean in terms of actual, hard numbers? A percentage is great and all... but how many Linux computers (Desktops and Laptops) are in operation?
Let's figure out exactly that using the best available data.
The Linux Marketshare Jump
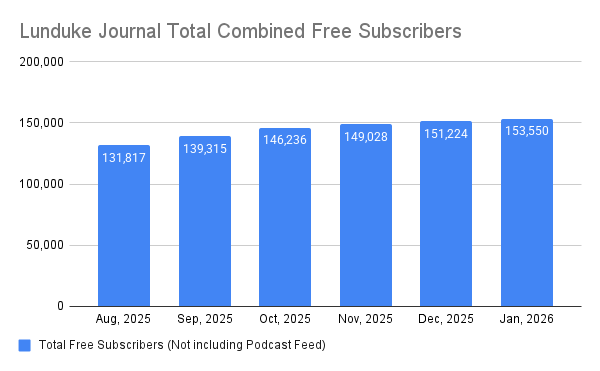
There's no denying it, Linux marketshare has risen significantly over the last year.
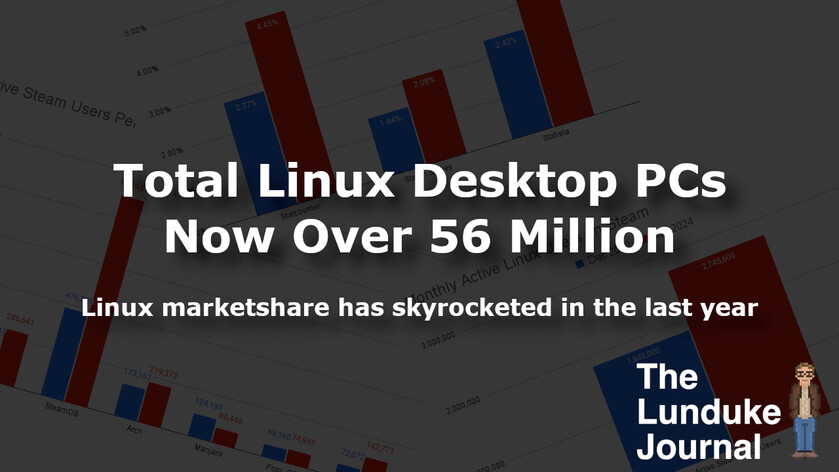
- Up to 4.45% according to Statcounter
- Up to 2.08% according to Steam
- Up to 4.03% according to Statista
Here's a chart showing the change between December of 2022 and July of 2024 -- a little over a year and a half.
That sort of marketshare percentage jump is impressive... but what does that translate to in terms of real, practical numbers?
How Many Linux PCs Are There?
Let's put the Steam numbers aside for a moment -- since that focuses entirely on a subset of gaming PCs -- and take a harder look at the details from Statcounter (4.45%) and Statista (4.03%).
Since we have a percentage marketshare range (4.03% - 4.45%), we need to have a rough idea of how many Desktop PCs there are out there. In total (including Windows, Mac, etc.). Not just shipping PCs... but total install base.
The best, most recent estimate we have for this data comes from Gartner -- and puts the total install base (world wide) of Desktop and Laptop PCs at roughly 1.399 Billion. The reality is, this number is likely a little low as we have seen mild growth in that segment since that report was published. Just the same, these numbers are the most accurate we have to work with... and should be pretty close to reality.
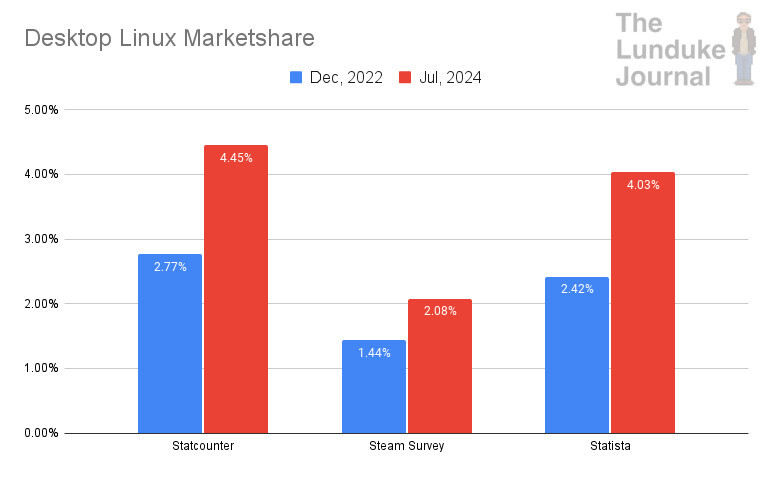
With that in mind, let's do some simple math and compare the total number of Desktop PCs (laptop and desktop) running Linux... in December 2022 and July 2024.
Oh, boy. That's a big jump in just a year and a half.
According to Statista:
- Dec, 2022: 33,855,800
- July, 2024: 56,379,700
According to Statcounter:
- Dec, 2022: 38,752,300
- July, 2024: 62,255,500
In other words: As of July of 2024, there are between 56 Million and 62 Million Linux-powered desktop PCs. Representing an increase of roughly 23 Million total installations.
What About Linux Gaming PCs?
Let's get back to the data from Steam... because knowing exactly how many Linux-powered PCs are being used for gaming is highly interesting.
We know that there are roughly 35+ Million peak online users of Steam...
But how many Monthly Active Users are there of Steam (ie. people who use Steam at least once per month)? The best data we have -- which is over one year old -- says there are roughly 132 Million Monthly Active Users.
While it would be nice to have more up to date numbers, that 132 Million number will provide us with a good starting point.
Now let's plug in the July, 2024 percentage (2.08%) and compare that to the Dec, 2022 percentage (1.44%).
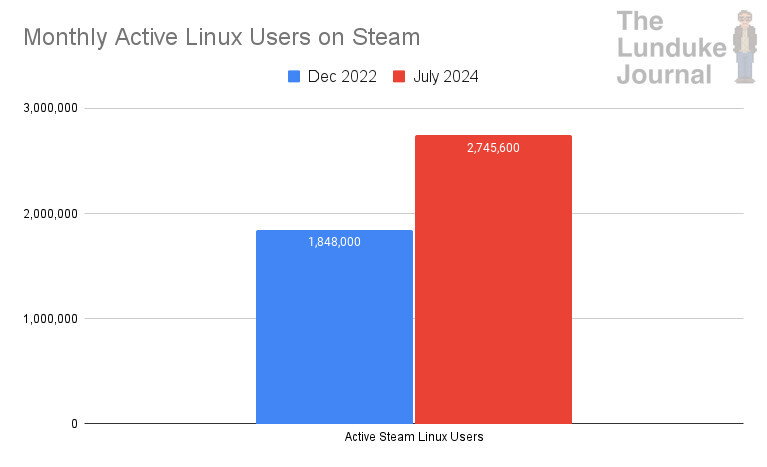
Total Linux PCs Using Steam:
- Dec, 2022: 1,848,000
- July, 2024: 2,745,600
While this increase, over the same time period, is not as impressive as what we see from the Statista and Statcounter numbers... going from 1.8 Million to 2.7 Million Linux gaming PCs is nothing to sneeze at.
Sure. This may represent a small fraction of the total PC gaming market. But 2.7 Million? For Linux?
Absolutely wild.
Back in "Ye Olden Times" of Linux, we were just happy to get sound working... and have one or two games that we could actually get running. To think that Linux is now a mainstream gaming platform with over 2.7 million installations used -- actively -- for gaming (using Steam)... is mildly mind-blowing.
Which Linux Distributions Are Being Used?
Measuring usage details of Linux distributions is notoriously difficult. Some Linux Distros provide unreliable, poorly sourced data... and others provide absolutely no details whatsoever (for a variety of reasons).
As an example, Ubuntu provides zero details around the actual number of installations or active users.
In fact... one of the most detailed statistic provided by Ubuntu is (and this is not a joke):
"More people use Ubuntu than anyone knows!"
Seriously. Here's a screenshot which also states "Hundreds of millions of PCs, servers, devices, virtual machines, and containers have booted Ubuntu to date" which... tells us almost nothing about how many PCs are running Ubuntu right now.
Luckily, Steam provides a breakdown of the most-used Linux distributions of their gaming platform. While that doesn't give us a detailed view of the total market... it does provide some interesting data.
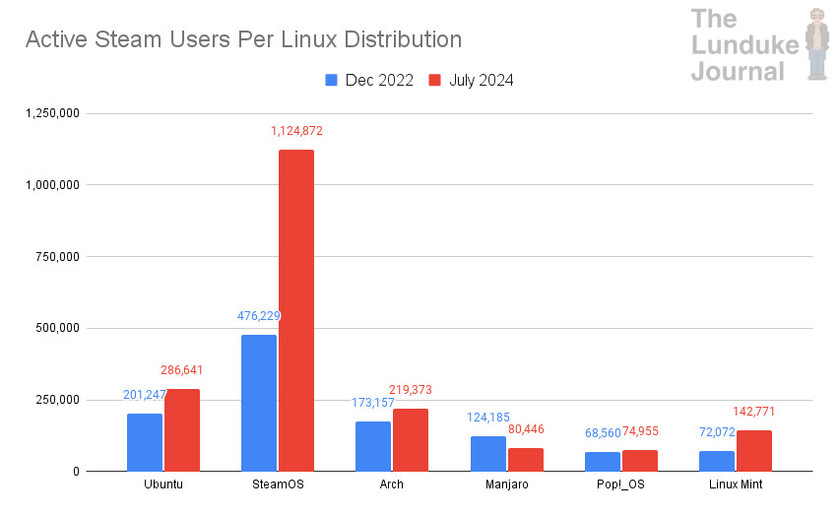
No surprise: SteamOS (based on Arch) is, by far, the most popular Linux distribution in use... by Steam. With the vast majority of the growth focused on that one Linux Distro.
Just the same, the other usage numbers are also rather fascinating. Noteworthy growth in Ubuntu, Arch, and Mint usage by Steam. Pop!_OS (from System76) remained somewhat stagnant, and Manjaro saw a significant drop (both in terms of percentage and real, total numbers).
Does any of that map -- in any real way -- to non-gaming Desktop PCs? Without detailed numbers from the major distributions (which we are unlikely to ever get), we don't have any way of knowing for certain.
What We Know About Linux Marketshare
So, as of July of 2024, what do we know about the real numbers regarding Linux marketshare?
- Between 56 Million and 62 Million PCs (Desktops and Laptops) running Linux.
- 23 Million additional Desktop PCs are running Linux as of July, 2024... compared to a year and a half earlier.
- 2,745,600 Linux PCs running Steam (and actively using it, every month).
- Nobody has a clue how many people use Ubuntu.