Linux (or, GNU/Linux, if you prefer) distributions are absolutely amazing. Stability, speed, flexibility; Your average Linux-based system is a veritable powerhouse of functionality – a tour de force of what computers can accomplish. But, from time to time, other operating systems have some pretty great ideas.
Here are 7 of my personal favorites that our favorite Linux distributions might want to consider… “borrowing”. Hint hint. Nudge nudge.
Mac OS Classic - Extensions

Back in Ye Olden Times – back before “MacOS X” was a thing – the classic Macintosh Operating System had a cool little feature called “Extensions”. These were, essentially, little TSR’s – programs that ran and stayed running in the background. The obvious usage for these were things such as device drivers, custom theme systems, and such. All of which can be accomplished on Linux just fine.
So why are Extensions so cool? It was all about how easy they were to manage. An Extension is a single file that you simply drag into your “Extensions” folder – next time you reboot, the extension is loaded. (Those icons along the bottom of the Mac OS boot screen? Those are Extensions.) Don’t want to use it anymore? Simply drag it out of that “Extensions” folder. Is one extension causing problems? Reboot holding down the Shift key – and all Extensions are disabled. Handy. Easy.
BeOS / Haiku - UI for per-thread priorities
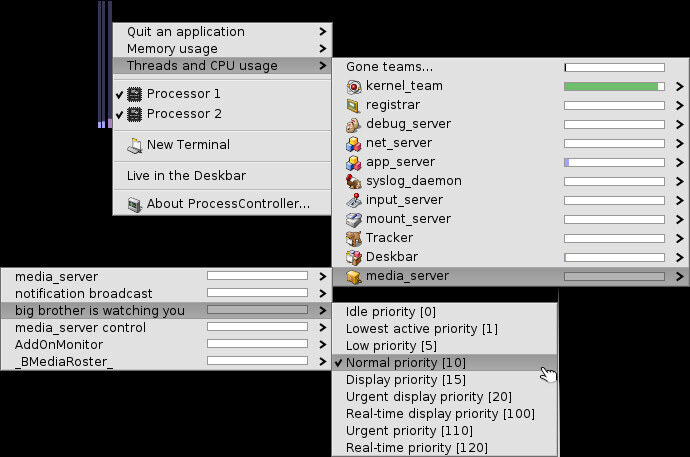
Being able to set the priority of running applications is nothing new. We’ve been using nice to set the priority of a task since Abraham Lincoln first sailed the Ocean Blue and discovered the printing press. The Operating System, Haiku, kicks it up a notch by providing a simple user interface which allows you set the priority level of every thread in every running task throughout the system with just a few quick clicks. This is made even more powerful by Haiku’s heavy emphasis on multi-threaded applications… but would still be beneficial on Linux.
Amiga - Icons of any size
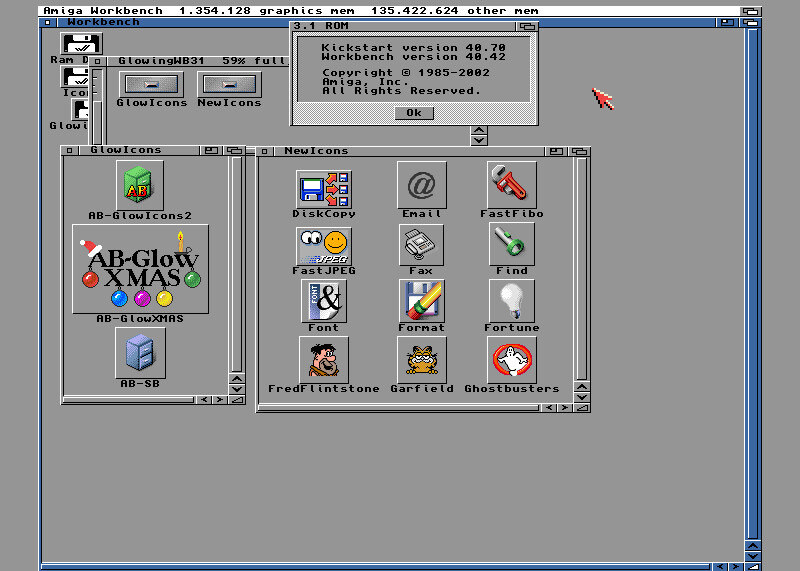
The ability to have icons be (essentially) any size you like may be a bit less practical than the previous two features… but it’s still a fun one. And we’re not talking a global “set the icon size” setting, here. The Amiga Workbench allows you to make each application have different sized icons. Some little. Some huge. Any size you like.
Mac OS Classic - AppleScript Everywhere
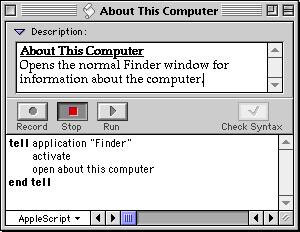
Mac OS has a scripting language known as AppleScript. And, while it is still in use today, its usefulness and prevalence is a tiny fraction of what it once was (because, I am pretty sure, Apple doesn’t like cool things anymore).
Back in the “Classic” Mac days (pre-OS X) almost every application had what is known as an “AppleScript Dictionary” – a set of publicly usable (and documented right in the application itself) API’s that allowed anyone to write a script to interact with and use graphical applications. Not only that, but a person could “record” a script by simply using an application (such as a word processor) while having a Script Editor in “record” mode. It was a godsend for automation.
In the UNIX/Linux world, we have this power in the shell with command line applications – but graphical applications on Linux, by and large, lack proper interfaces for doing any real scripting. And, considering the “maker / developer / pro-user” roots of Linux… it seems like a glaring oversight and design problem with most GUI applications.
Mac OS Classic - Easy RAM Disk
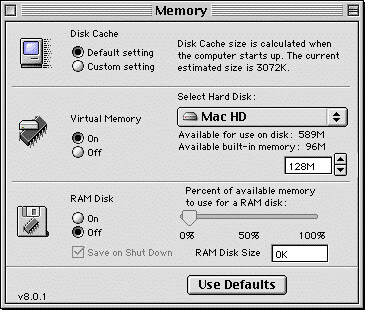
That’s right. Another feature of the classic (pre-OS X) Mac OS. It was a system with many (many) flaws, but it also had some really cool features. One of those being how it handled RAM Disks. Open up the “Memory” control panel. Turn on the RAM Disk. Set the size. And then select if you’d like the contents to be preserved (to the drive) when rebooting. Crazy easy to do.
Why would you want this, you ask? Want to increase the speed of a game or utility that needs to read/write to the disk a lot? Toss it in a Ram Disk and it’s now running entirely from RAM. The speed improvement can, oftentimes, be dramatic. Plus you won't be writting to that SSD quite so often.
Mac OS (Classic and X) - Applications in a single file

The traditional Linux repository model is, without a doubt, incredibly powerful… but having applications that exist, with all of their supporting data (and libraries), within a single file can be incredibly handy. No if’s or but’s about it. Mac OS (classic) handled this by jamming all data for an application into what was classically called a “resource fork” (often edited with a tool known as ResEdit).
Mac OS X does something similar by storing all of that data within a predefined folder structure with a “.app” extension – thus showing it to the end user as if it were just a single file. Linux projects such as AppImage are slowly filling this need, but we’ve yet to see this really be embraced by the mainstream Linux distributions in any significant way.
Mac OS Classic - Control Strip
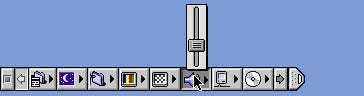
Another classic Mac OS oddity that proved useful: The Control Strip. A movable, collapsible, expandable, bar that provided quick access to a lot of commonly used bits of functionality. Volume, display, media playback, network drives… that sort of thing. The truly nice part of the Control Strip was that I could place it wherever I liked and shrink it to get it out of my way when I don’t need it.
There you have it. Seven pretty nifty features that would be awesome to have on Linux. Technically, some of these features are already available on Linux (such as with AppImage)… but few Linux-based Operating Systems are currently using and taking advantage of them.