I absolutely love the computers of the old Soviet Union.
Sure, I never had one: I never lived in the Soviet Union… and I don’t speak a single drop of Russian.
Just the same, there’s something fascinating and wild about the computer industry of that particular place and time.
The Soviet-styled, Sci-Fi inspired cases. The (often) knock-off copies of hardware and (also often) stolen ROMs and software. The history, technology, and aesthetics are downright whimsical.
Presented here are two of my absolute favorites: The Iskra 1256 and the Agat 4.
Special thanks to the Soviet Digital Electronics Museum for providing images for so many (often difficult to track down) Soviet-era computers.
Iskra-1256 (1979)
While the Iskra 1256 was technically created in 1979… it didn’t really see production until 1980. So it qualifies as a 1980s computer, in my book.
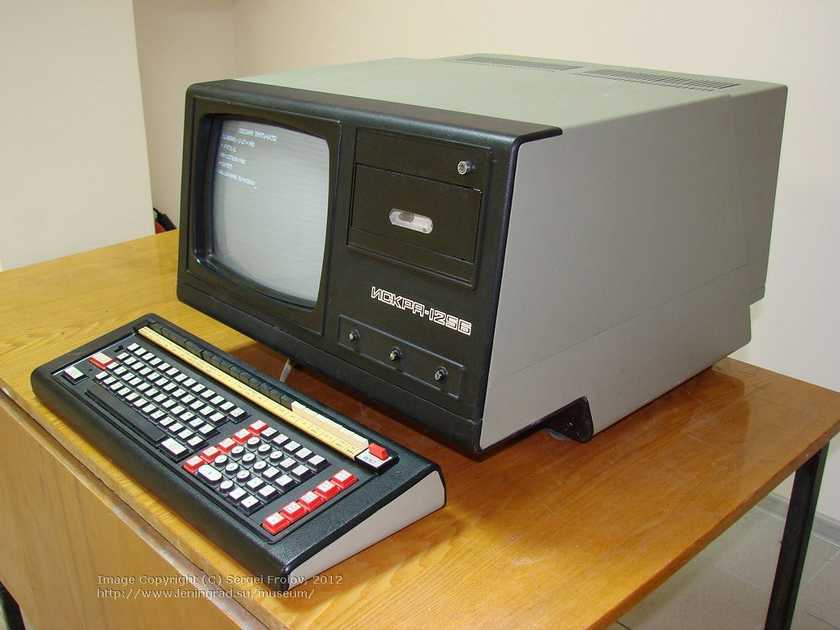

First off: Just look at that keyboard. It has a distinct Soviet Sci-fi look to it, which is pretty darn cool.

Also fascinating is the internal design. It used a series of (mostly removable) boards aligned in vertical panels — and was powered by a 16 bit CPU clocking in at 3 MHz. The base RAM was 4 KB, expandable to 64 KB. Not too shabby for the early 1980s!

Also interesting: It shipped with a BASIC-like programming language. Essentially it was similar (in some respects) to Tiny BASIC… only, you know, in Russian. Here’s an example:

While I have been unable to discern exactly which processor the Iskra 1256 used, a reasonable guess would be something akin to the Texas Instruments TMS9900 — a 16bit CPU, released in 1976, that was also used in the TI-99/4A… which clocks in at the exact same speed.

Whether it is the same CPU, a Soviet clone, or some other (similar) CPU remains unclear.
One other interesting design choice that I quite like: A built-in cassette reader for loading and saving data… right on the front of the main unit. So many personal computers of this era opted to use external cassette decks — often connected to a dedicated “datasette” port. It’s rare that you find a cassette reader directly built in.

This PC was in regular usage throughout the 1980s. In later years multiple languages were ported to the machine — including a true BASIC, Fortran, and Algol.
It was, truly, one heck of a machine.
And it had a cost to match.
14,200 Rubles. Which means this machine had a cost of — quick math on the back of a napkin — over $9,000 USD in the mid 1980s. Phew. Not a cheap machine! Though it wasn’t for sale in the USA anyway… so, even if I could have afforded one, it wouldn’t have been available to me.
Agat-4 (1983)
A few years later, in 1983, an Apple II clone was produced with an absolutely wild design… the Agat 4.
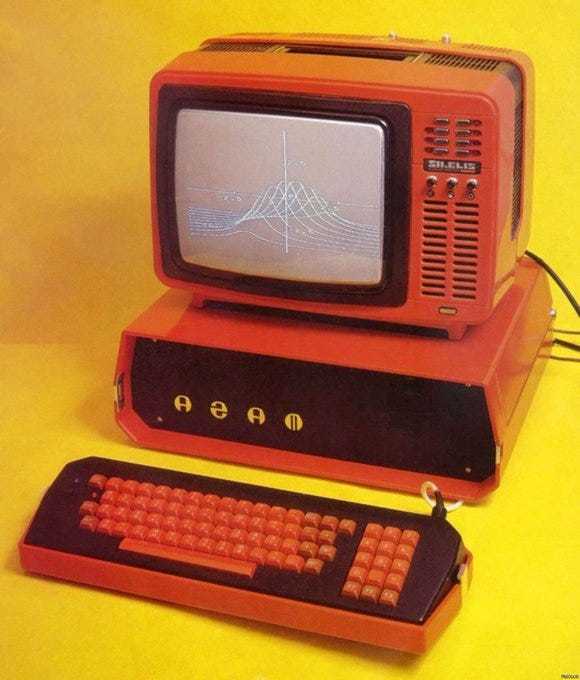

Despite the extremely different appearance, the guts of the Agat 4 were incredibly close to that of an Apple II. Same MOS 6502 CPU. 64 KB of RAM. In so many ways… this is a crazy, orange, desktop form-factor, Sci-Fi looking Apple II.
It even used a slightly modified copy of the Apple II ROM.
Seriously.
Supposedly you can even find Wozniak’s name (the creator of the Apple II and Apple II ROM) inside the ROM bits for the Agat-4.

The unit came in three parts:
A standard (but cool looking) color SECAM television.
The main case (which included the power supply, CPU, RAM, and a single 5 1/4” floppy drive).
And a detached keyboard.
SECAM is an analog TV standard that was commonly used in France, Russia, and a few parts of Europe and Africa. Similar (in many respects) to the PAL or NTSC standards. 50 Hz refresh rate (same as PAL, whereas NTSC is 60 Hz). Likewise SECAM has the same resolution as PAL. That said, where SECAM differs is that the Red and Blue colors are sent alternately… as opposed to being sent together in both NTSC and PAL signals.
There was an optional cassette port (for loading software off an external cassette player) and a printer port. Other than those, there weren’t any expansions available. RAM was locked at 64 KB. And there was no option to add a second floppy drive.
You’ll have one floppy drive and you’ll like it!

Many nicknamed this system “Yablotchko”. Which, supposedly, means “Little Apple”. A fact that the translation website I just used verified.
Despite being an obvious Apple II functionality clone (with a clearly modified Apple II ROM), the Agat 4 suffered from compatibility problems with standard Apple II software. Some applications and games would run… but many would not.
This was thanks, in large part, to the way the the engineers of the Agat 4 hacked the Apple II ROM to add in cyrillic characters, as well as minor differences in hardware design.
Later models in the Agat line would improve the Apple II compatibility… even going so far as to offering an (optional) “Apple II” compatibility card. Unfortunately, later models stopped using the awesome, orange form factor.

The Soviet Union wanted to sell the Agat line in other nations. Unfortunately that didn’t go very far… as each computer was priced around $17,000 USD. Seriously. For an Apple II clone.
Making the Agat 4 one of the most expensive personal computers in world history.
Hey. The color orange ain’t cheap!
The LEGO Agat 4
Speaking of that awesome, orange design… someone created a LEGO model of an Agat 4. And it is absolutely glorious.