A new lawsuit against Intel Corporation, filed by an ex-employee, paints a picture of a company which is distinctly anti-Jewish and anti-Israeli.
According the lawsuit:
- One Intel Vice President (and multiple Intel employees) openly praised the murder of Israelis and Jews.
- Intel responded to a Jewish Israeli employee having his family's home hit by a rocket from Hamas... by reassigning that Jewish employee to report directly to the Vice President who was praising rocket attacks against Israelis.
- Intel fired that Jewish employee for complaining about working for a man who calls for the death of him and his family.
- Intel replaces that Jew with another man who openly attacks Israel.
The Lunduke Journal has reached out to Intel for comment but, as this is an ongoing lawsuit, no response is expected.
You can read the entirety of the suit, but let's go through some of the high level points -- they paint a fairly horrifying picture of the upper level of management within the company.
John Doe v Intel Corporation

After the October 7th, 2023 attacks by Hamas -- including the murdering, beheading, and raping of men, women, and even babies within Israel -- an Intel executive (Alaa Badr, previously at VMWare) took to social media to proclaim his support for Hamas -- and his desire to see Jews and Israelis murdered.
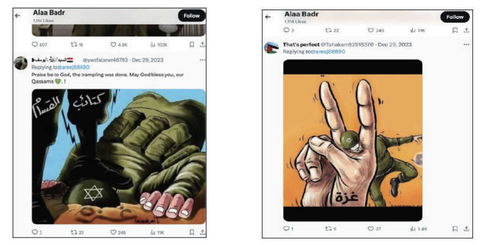
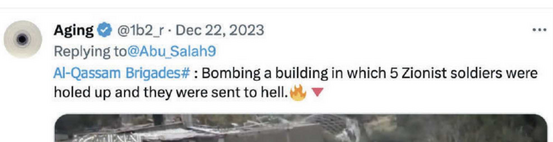
This included "liking" and sharing numerous social media posts glorifying violence against Jews -- such as "Praise be to God, the trampling was done" with a boot on the neck of a Jew.
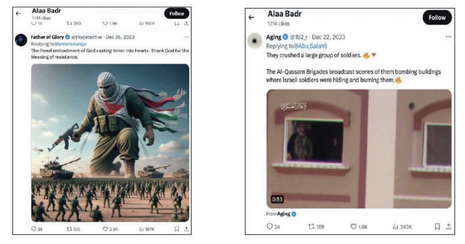
With other posts celebrating the burning of Israeli soldiers and declaring they would be "sent to hell".
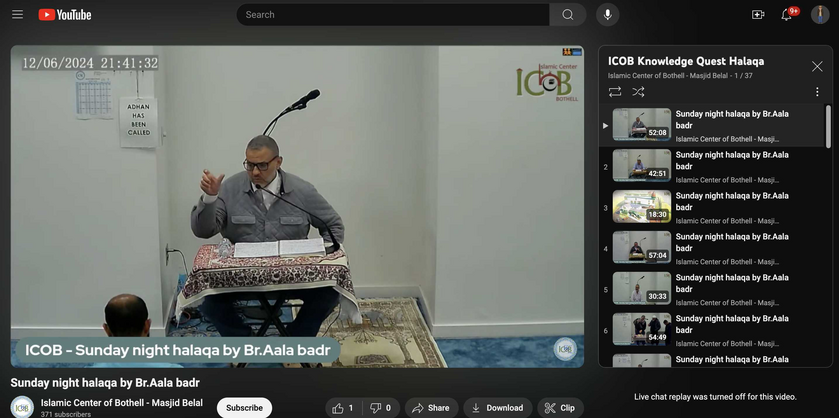
Alaa Badr, Vice President of Customer Success out of the Seattle offices of Intel Corporation, is a prominent member of the Islamic Center of Bothell -- where he gives weekly lessons (halaqa), often discussing Jews and Israel.
According to the suit, Intel was made aware that Alaa Badr (a VP) was wishing death upon Israelis. Badr's hatred of Israelis, according to the suit, was well known within the company.
Here's where the story gets truly insane.
The plaintiff in this lawsuit -- who is simply identified as "John Doe" -- is an Intel executive... who is a Jewish Israeli citizen, living in the USA, and a former member of the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF). John Doe's family home, in Israel, was hit by rocket fire from Hamas, which nearly killed almost his entire family.
Intel HR and executives were made aware of that rocket strike on John Doe's family.
While that was happening, Vice President Alaa Badr was publicly praising the death of Israelis from the Hamas attacks.
Then, on January 29th, 2024, John Doe was reassigned... with Alaa Badr as his new boss.
This really and truly happened. In response to a Jewish, Israeli employee of Intel having his family attacked -- with a rocket -- by Hamas... Intel Corporation, almost immediately responded by moving that Jewish employee to now work directly for a man who expresses his public hatred for Jews and Israelis... literally wishing death on them.
According to the suit:
"Badr was not shy about his antisemitic views even with John Doe himself. Badr repeatedly pressured John Doe to tell him whether other Intel employees were Israeli. When John Doe confirmed that specific employees were Israeli, Badr sneered that there were 'so many Israeli employees in our company.'"
A formal complaint was filed regarding Badr with Abdul Jarrar -- Badr's boss, and an Intel VP who has been with the company for 26 years -- but no action was taken against Badr.

Which means that John Doe, according to the suit, "continued to report to a man who would like to see his family murdered. Intel did literally nothing to protect John Doe."
At which point, John Doe -- the only Israeli on Badr's team -- was fired:
"Indeed, shortly after the aforementioned follow-up complaint, in March 2024, Badr viewed John Doe’s LinkedIn profile, which identifies John Doe as a former IDF soldier. Just a few weeks later, on April 2, 2024, Jarrar informed John Doe that his employment was being terminated..."
Then, Intel hired the replacement of John Doe.
Who do they get to replace the Jewish man?
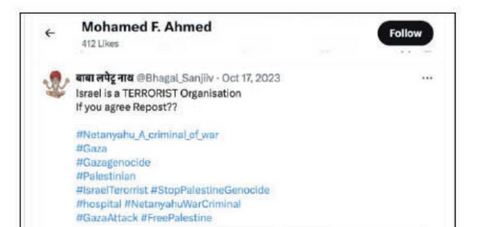
Another person who only expresses hate for Israel and support for Hamas.
"The unlawful motives behind John Doe’s termination could not have been more clear when, just weeks later, Badr and his supervisor, Jarrar, hired John Doe’s replacement: Mohamed Ahmed (“Ahmed”). Incredibly, Ahmed openly espoused the same anti-Israel sentiments as Badr."
Absolutely wild.
That's right. Intel moved a Jew -- whose family was being hit by rockets from Hamas -- to work directly for an Intel VP who was praising those very same attacks. Then, when the Jewish man complained even a tiny bit, Intel fired him and replaced him with someone else who hates Israel.
What is Intel doing?
Based on a quick search (including LinkedIn profiles), it would appear that both Mohamed Ahmed and Abdul Jarrar continue to work at Intel.
It is difficult to know if Alaa Badr continues to be employed by Intel as he has deleted his LinkedIn account entirely.
Just the same, Intel has made no mention of Alaa Badr being fired. And, considering he is a Vice President... the lack of announcement suggests he is possibly still with Intel (at least in some capacity).
Now... it is standard practice for a company to not comment on active legal actions. As such it is highly unlikely that we will hear anything from Intel regarding this.
That said, this is a very, very big deal. One which Intel needs to get on top of very quickly. Both privately and publicly.
Intel simply wouldn't be Intel without early Jewish employees. Dov Frohman (who lost his parents in the Holocaust) is the inventor of the EPROM. And, of course, Andy Grove (whose father was held captive and tortured in a Labor Camp by the Nazis) was one of the first employees of Intel (and eventually the CEO).
But has Intel changed? Is Intel no longer a safe place to work for Jews or Israelis?
If even a portion of this lawsuit is accurate, it suggests exactly that.
And the ramifications for Intel employees, along with large portions of the Tech Industry, could be extreme. At a time when Intel is already experiencing significant negative press -- including mass layoffs -- this is certainly not the kind of attention that the company needs.