Powerful, “Command Line” computer interfaces have been around for — what seems like — forever. Interfaces where you can run multiple commands, one after another (in a batch)… where you can have simple “scripts” to tie those commands together.
That sort of “Shell” comes in so many forms… from SH and BASH on UNIX-like (and Linux) systems… to COMMAND.COM and PowerShell on Windows.
The text “Shell” is everywhere. And has been for longer than most can even remember.
But it had to start somewhere. Someone had to make the first “Shell”.
This is that story.
And that story starts… with a man. His name is Louis Pouzin.
The Man
Louis Pouzin was born, in 1931, in a small town in almost the smack-dab-middle of France: Chantenay-Saint-Imbert.

In the 1960’s Pouzin would move from France — and his job managing programmers at Bull (a French computer company) — to Massachusetts. His new job would put him working on an ambitious computing project at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology…
The Compatible Time-Sharing System
In 1961, the world’s first, general purpose, time sharing operating system was demonstrated at MIT.
That system — the “Compatible Time-Sharing System”… or “CTTS” — was originally developed on an IBM 709. And oh, what a beautiful machine it was.
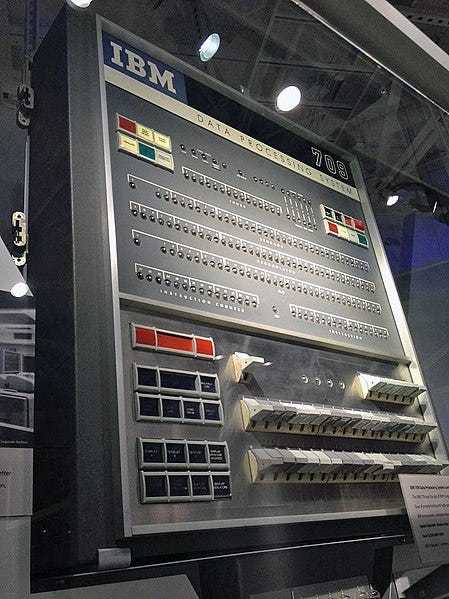

The IBM 709 was an absolute beast. Capable of adding 42,000 numbers per second, and multiplying two 36-bit integers together at a (then) blinding speed: 5,000 per second.
All contained in a svelte 2,000 pounds.
And this IBM 709, running CTTS, certainly had a text interface… but it wasn’t exactly a “Shell”. At least not in any way we would recognize together. Certainly, no scripting together of commands.
Over the next two years, CTTS continued to improve and evolve. Getting ported, by 1963, to a modified IBM 7094. Which, like the 709 before it, was a gorgeous machine. With enough physical switches to make any Sci-Fi nerd happy.
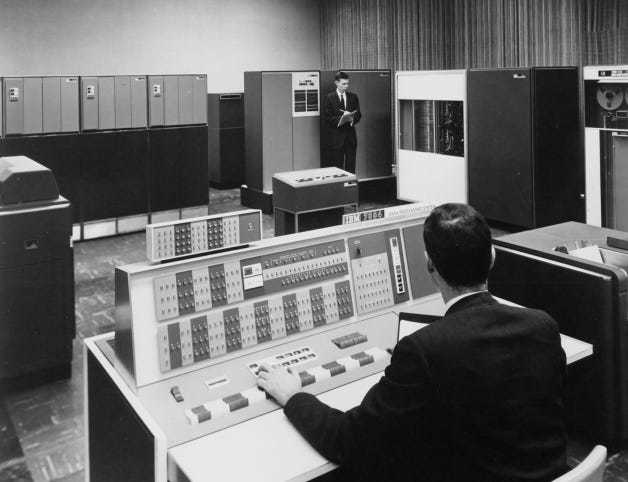

It is around this time, that Pouzin arrives at MIT, where he is (at least partially) responsible for a little program called “MAIL”.
Wait. What? Pouzin invented E-Mail?
Well. Not quite. This was several years before what we now call “E-Mail” was created. This original “MAIL”, on CTTS, was a system for sending mail messages to other users… on the same CTTS system. It lacked a mechanism for forwarding messages to users on other systems.
Just the same, this work heavily influenced what would later become “E-Mail”.
But we’re not here to talk about MAIL or the many contributions Pouzin made to computer networking (leading to what we call “The Internet”) — that’s a fascinating topic for another day. Let’s focus on a little program that Pouzin wrote… which would change computing forever.
RUNCOM
You see, in those days, there was no “command interpreter” program. No “shell”. You simply instructed the kernel to run a single program.
Nothing like “COMMAND.COM” on DOS. Or BASH, SH, or other shells on UNIX and Linux systems. Nothing at a all like that existed.
That all changed in 1963, when Pouzin came up with “RUNCOM” — short for “RUN COMmand”.
In Pouzin’s words:
“After having written dozens of commands for CTSS, I reached the stage where I felt that commands should be usable as building blocks for writing more commands, just like subroutine libraries. Hence, I wrote "RUNCOM", a sort of shell driving the execution of command scripts, with argument substitution. The tool became instantly most popular, as it became possible to go home in the evening while leaving behind long runcoms executing overnight. It was quite neat for boring and repetitive tasks such as renaming, moving, updating, compiling, etc. whole directories of files for system and application maintenance and monitoring.”
RUNCOM was, truly, the first “Shell” system.
In fact, Pouzin, was the first person to call such a program a “Shell”.
His RUNCOM program would continue to be a critical component of the CTTS system until it ceased operations in 1973.

But we still didn’t quite have what we would call a “Shell”. Not yet.
The “Shell” had a name, and some of the features, but it wasn’t a truly interactive experience.
Meanwhile, in England…
During 1964, a computer scientist named Christopher Strachey was working at the University of Cambridge… on, what he called, the “General Purpose Macrogenerator”. Or “GPM”, for short.

This language had a heavy influence on much of 1960s and 1970s computing — including on “m4”.
M4 is a macro language, developed by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie, that was part of the original version of UNIX… and was later adopted as a part of the POSIX standard.

Back in Massachusetts…
During 1964, work on Multics (the “Multiplexed Information and Computing Service”) was getting underway at MIT (as a joint project between MIT, General Electric, and Bell Labs).
While Pouzin wasn’t going to be part of the Multics project… boy howdy… he had some ideas.
In his own words:
“Then in 64 came the Multics design time, in which I was not much involved, because I had made it clear I wanted to return to France in mid 65. However, this idea of using commands somehow like a programming language was still in the back of my mind. Christopher Strachey, a British scientist, had visited MIT about that time, and his macro-generator design appeared to me a very solid base for a command language, in particular the techniques for quoting and passing arguments. Without being invited on the subject, I wrote a paper explaining how the Multics command language could be designed with this objective. And I coined the word "shell" to name it. It must have been at the end of 64 or beginning of 65.”
Pouzin made sure his ideas were documented, by publishing a document entitled: “The SHELL: A global tool for calling and chaining procedures in the system”.

According to Pouzin:
“The small gang of Multics wizards found it a sleek idea, but they wanted something more refined in terms of language syntax. As time left to me was short, and I was not an expert in language design, I let the issue for them to debate, and instead I made a program flowchart of the shell. It was used after I left for writing the first Multics shell. Glenda Schroeder (MIT) and a GE man did it.”
From Tom Van Vleck, who worked on Multics for 16 years (starting in 1965):
“The first time I remember the name "shell" for the function of finding and running a command was in a Multics Design Notebook document by Louis Pouzin.
These memos con[t]ained the idea of having the command processing shell be an unprivileged user program that parsed a command line, located a program to run, and executed it with arguments.”
So. Who created the first “Shell”?
The concept, and first implementation of a “Shell” (RUNCOM for the CTTS), was made by Louis Pouzin.
But the first truly interactive example of a Shell — the one that was part of Multics, and which would most closely resemble the interactive shells of today — was initially designed by Pouzin… and programmed by Glenda Schroeder and a “Mystery Man from General Electric”.
The impact of RUNCOM and the Multics Shell
The impact of these early Shells cannot be understated.
Because of RUNCOM — and the designs of Pouzin — we have the Multics Shell.
Because of Multics… we have UNIX (originally named UNICS… before someone in marketing decided an “X” looked cooler) and SH.
You can trace every single computer Shell in existence — including BASH, PowerShell, and so many others — back to that first work. Back to the ideas of Louis Pouzin.
In fact, that influence expands far beyond just the design ideas of a scriptable, interactive Shell.
According to Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie:
"There was a facility that would execute a bunch of commands stored in a file; it was called RUNCOM for "run commands", and the file began to be called "a runcom". rc in Unix is a fossil from that usage."
That’s right. Have you seen “rc” on your UNIX or Posix systems — such as .cshrc or /etc/rc? Those are named that way, according the the men behind UNIX itself, because of RUNCOM and Louis Pouzin.
To put it simply, modern computing is the way it is, in large part… thanks to Pouzin. A computer scientist that should be a household name.